TM 5-3820-245-14&P
ENGINE COOLANT
The coolant provides a medium for heat transfer and
To determine if a particular water is suitable for use as a
controls the internal temperature of the engine during
coolant when properly inhibited, the following
operation. In an engine having proper coolant flow, the
characteristics must be considered: the concentration
heat of combustion is conveyed through the cylinder
walls and the cylinder head into the coolant. Without
dissolved solids.
adequate coolant, normal heat transfer cannot take place
within the engine, and engine temperature rapidly rises.
Chlorides and/or sulfates tend to accelerate corrosion,
In general, water containing various materials in solution
while hardness (percentage of magnesium and calcium
is used for this purpose.
salts broadly classified as carbonates) causes deposits
of scale. Total dissolved solids may cause scale
The function of the coolant is basic to the design and to
deposits, sludge deposits, corrosion or a combination
the successful operation of the engine. Therefore,
coolant must be carefully selected and properly
PARTS PER
GRAINS PER
MILLION
GALLON
maintained.
Chlorides (Maximum)
40
2.5
COOLANT REQUIREMENTS
Sulfates (Maximum)
100
5.8
Total Dissolved Solids (Maximum)
340
20
Coolant solutions must meet the following basic
Total Hardness (Maximum)
170
10
requirements:
TABLE 1
1. Provide for adequate heat transfer.
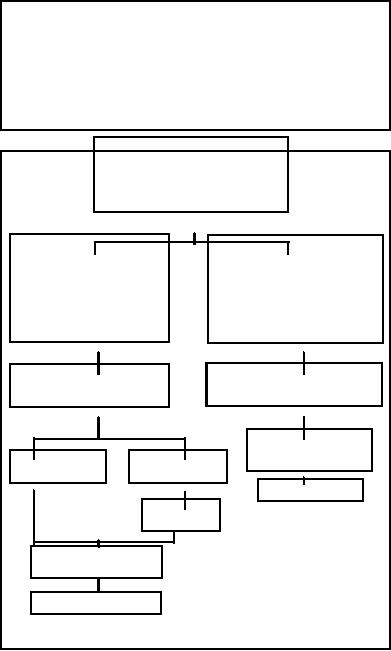
Determine The Concentrations
2. Provide a corrosion-resistant environment within the
of Chlorides, Sulfates, And
cooling system.
Total Dissolved Solids
In The Water
3. Prevent formation of scale or sludge deposits in the
cooling system.
Chlorides Under 40 ppm
Chlorides Over 40 ppm And
And
Or
4. Be compatible with the cooling system hose and seal
Sulfates Under 100 ppm
Sulfates Over 100 ppm
materials.
And
Or
Total Dissolved Solids
Total Dissolved Solids
5. Provide adequate freeze protection during cold
Under 340 ppm
Over 340 ppm
weather operation.
Determine Total
Distill, De-mineralize
The first four requirements are satisfied by combining a
Hardness Of The Water
Or De-ionize The Water
suitable water with reliable inhibitors. When freeze
protection is required, a solution of suitable water and an
antifreeze containing adequate inhibitors will provide a
Water Suitable For
satisfactory coolant. Ethylene glycol-based antifreeze is
Total Hardness
Total Hardness
Use in Coolant
recommended for use in Detroit Diesel engines.
Under 170 ppm
Over 170 ppm
Plus Inhibitors
Soften
WATER
The Water
Any water, whether of drinking quality or not, will produce
Water Suitable For
a corrosive environment in the cooling system, and the
Use In Coolant
mineral content may permit scale deposits to form on
internal cooling system surfaces.
Therefore, water
Plus Inhibitors
selected as a coolant must be properly treated with
inhibitors to control corrosion and scale deposition.
TABLE 2
PAGE 164

