TM 5-3820-245-14&P
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM MAINTENANCE
Engine Coolant
The function of the engine coolant is to absorb the heat, developed as a result of the combustion process in the cylinders,
from the component parts such as exhaust valves, cylinder liners and pistons which are surrounded by water jackets. In
addition, the heat absorbed by the oil is also removed by the engine coolant in the oil-to-water oil cooler.
For the recommended coolant, refer to Engine Coolant.
Cooling System Capacity
The capacity of the basic engine cooling system (cylinder block, head, thermostat housing and oil cooler housing) is shown
in Table 1.
To obtain the complete amount of coolant in the cooling system of an engine, the additional capacity of the radiator, hoses,
etc. must be added to the capacity of the basic engine. The capacity of radiators and related equipment should be
obtained from the equipment supplier.
Fill Cooling System
Before starting an engine, close all of the drain cocks and fill the cooling system completely. If the unit has a raw water
pump, it should be primed, since operation without water may cause impeller failure.
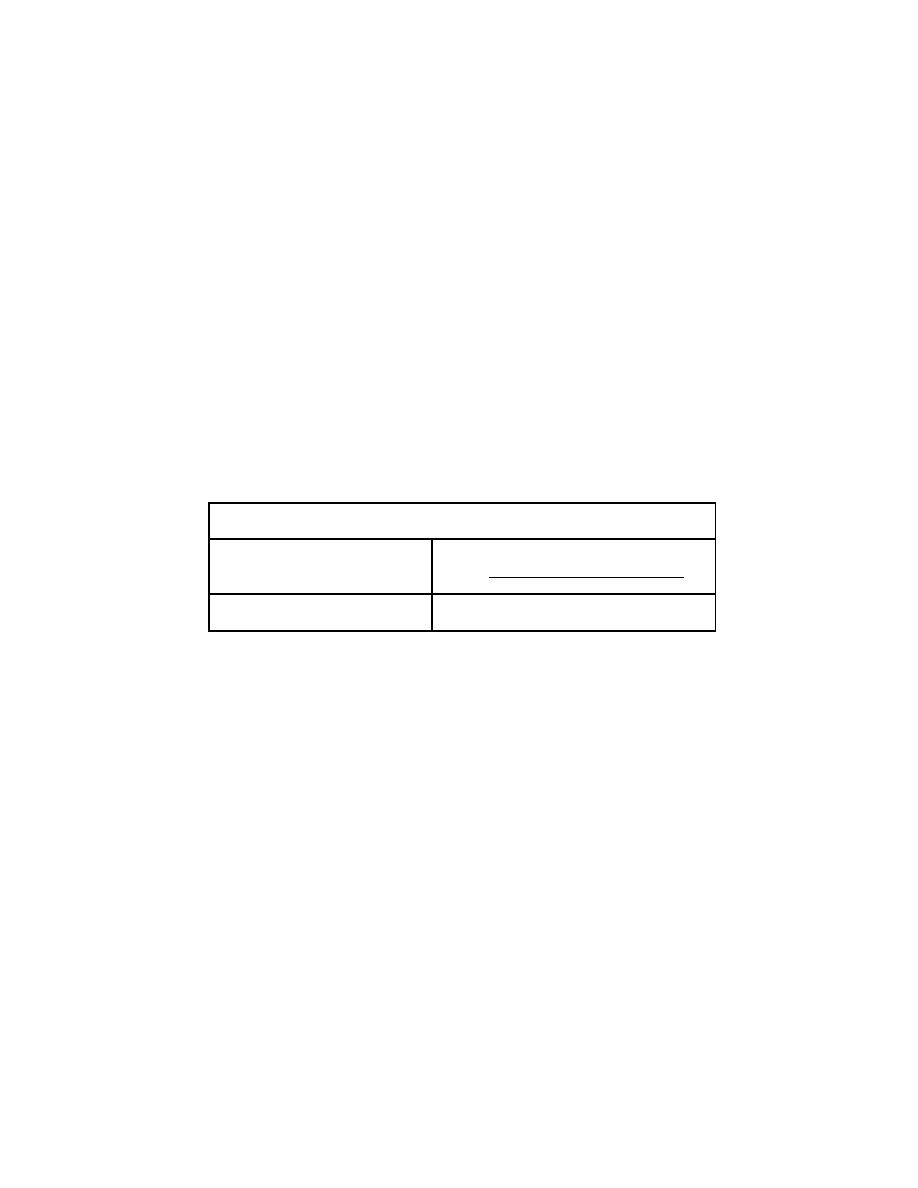
COOLING SYSTEM CAPACITY CHART
(BASIC ENGINE)
ENGINE
CAPACITY
Quarts
Liters
3-53
87
7.6
TABLE 1
Start the engine and, after normal operating temperature has been reached, allowing the coolant to expand to its
maximum, check the coolant level. The coolant level should be within 2" of the top of the filler neck.
Should a daily loss of coolant be observed, and there are no apparent leaks, there is a possibility of gases leaking past the
cylinder head water seal rings into the cooling system. The presence of air or gases in the cooling system may be
detected by connecting a rubber tube from the overflow pipe to a water container. Bubbles
PAGE 131


